Table of Contents
- 1 TSMC and Intel Net Income Comparison 2001 Q1 to 2024 Q2
- 2 TSMC dominates Intel in the semiconductor foundry market.
- 3 Intel Re-entered the Semiconductor Foundry Market in 2021 to Compete with TSMC
- 4 Intel Expands Outsourcing to TSMC
- 5 Intel missed the opportunity to secure a major contract with Sony for PlayStation due to high production costs.
TSMC and Intel Net Income Comparison 2001 Q1 to 2024 Q2
In the animation, we compared the quarterly net profits of the two leading semiconductor foundries in the world, TSMC and Intel, covering the period from the first quarter of 2001 to the second quarter of 2024. It can be seen that, for most of the time before around 2020, Intel’s net profit was greater than TSMC’s. In fact, Intel dominated the computer chip market for several decades with its well-known i-series chips, including the i3, i5, i7, and the high-end i9 chips. Currently, Intel is still a major leader in computer chips, but it also faces rising competition, such as AMD chips, which are manufactured using TSMC’s foundry services. Personally, I bought an Acer gaming laptop equipped with an AMD Ryzen processor.
Processors and related chips for desktop and laptop computers account for 40% to 50% of Intel’s total revenue.
Other revenue sources for Intel include data centers and AI, which make up about 30% of its revenue, networking and edge computing, which account for about 15% to 30% of its revenue, and high-performance graphics processors (GPUs), which represent about only 5%. The GPU market is mainly dominated by Nvidia, and Intel also offers semiconductor foundry services.
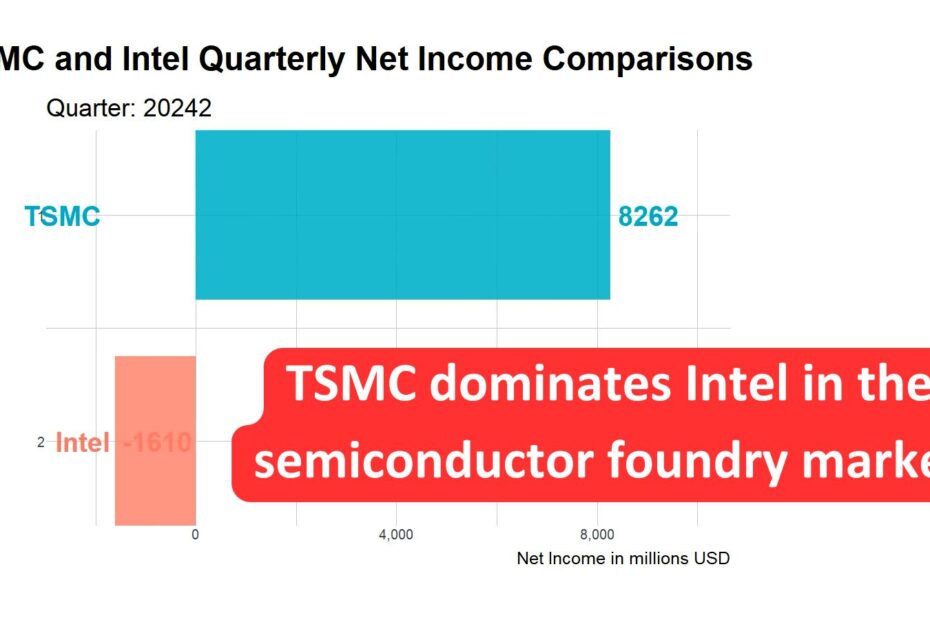
TSMC dominates Intel in the semiconductor foundry market.
In general, Intel provides an all-in-one service for semiconductor design and manufacturing, while TSMC focuses solely on foundry services. Since the second quarter of 2022, TSMC’s net profit has surpassed Intel’s for two consecutive years, purely through its foundry services. Intel, in fact, posted losses in the first two quarters of this year, while TSMC has maintained profitability every quarter for over 23 years, which is remarkable. In the most recent quarter, Q2 2024, TSMC’s net profit was $8.2 billion, while Intel had a loss of $1.6 billion. This teaches us an important lesson: focusing on excelling in a single area can create a strong and lasting competitive advantage. Later, we will share two more stories about how TSMC outperforms Intel, but for now, let’s first discuss why Intel is returning to the foundry market.
Intel Re-entered the Semiconductor Foundry Market in 2021 to Compete with TSMC
Intel’s key moment of re-entry into the foundry market was in 2021, when the company announced the launch of its new business unit, Intel Foundry Services (IFS). This was a strategic move for Intel to enter the foundry market on a large scale, with the goal of competing with leading foundries like TSMC and Samsung.
1. Background and Goals:
- Announcement date: In March 2021, Intel’s new CEO, Pat Gelsinger, introduced this plan as part of a broader strategic reorganization called the IDM 2.0 strategy.
- Main goals: Intel aims to expand into the foundry market by opening its manufacturing capabilities to other semiconductor design companies, reducing its dependence on key competitors like TSMC and Samsung. Additionally, Intel seeks to expand its global manufacturing footprint, particularly by building more fabs in the U.S. and Europe and securing government funding and support.
2. Competition and Challenges:
- Competitors: TSMC and Samsung have already established strong leadership in the foundry market. TSMC holds over 50% of the global foundry market share, while Samsung focuses on high-performance processes. Intel’s challenge is to quickly improve its manufacturing technology and close the gap with these companies.
- Technological gap: TSMC and Samsung are ahead in advanced process technologies, such as 5nm and 3nm processes. However, Intel is accelerating its technological advancements, aiming to catch up with its competitors’ advanced processes by 2024.
Welcome to Sunfortzone, our goal is to help value investors understand more about their investments and become a better person.
If you want to grow on the path of value investing, please subscribe to our Youtube channel to get more valuable contents in the future.
Wall streets make money on activities, we, as value investors, make money on inactivities.
Intel Expands Outsourcing to TSMC
Intel has abandoned its 20A process, originally planned for the Arrow Lake processors, which were expected to launch in 2024. Instead of using its own Intel 20A process, Intel will outsource production to TSMC and only handle the final packaging in-house. The company claims this move will save $500 million and allow it to focus resources on the more promising 18A process.
The Intel 20A process was considered a transitional step for the company. Compared to the first-generation node that introduced RibbonFET and PowerVia technologies, the second-generation Intel 18A node, which will use High-NA technology, is more mature and has better yields. Intel stated that its 18A PDK 1.0, released in July, has received positive feedback, and customers are expected to complete tape-out in the first half of 2025. The company also emphasized during its earnings call that the Panther Lake (18A process) processors, slated for the second half of 2025, will establish a competitive lead and improve profitability.
In the short term, improving cash flow is a top priority. Adjusting operations at its most loss-making fabs will help Intel remain afloat. Although outsourcing Arrow Lake may face the same outcome as Lunar Lake—where despite having competitive computing power, high costs will weigh down the company’s profit margins—Intel had already planned to outsource the high-end Arrow Lake production to external foundries while keeping the mid- and low-end Arrow Lake production in-house. Therefore, abandoning the 20A process will have a relatively minor impact on the company.
Focusing on the 18A process is a good strategy that extends Intel’s competitive timeline, with the potential for overtaking rivals in the future. However, the company still faces several challenges:
- It is difficult to completely separate Intel’s fabs from its chip design division. Competitors may be hesitant to risk technology leakage by outsourcing production to Intel’s foundries.
- With insufficient production volumes and fabs primarily located in the U.S. and Europe, Intel will struggle to lower costs.
- The 18A technology still needs close observation. While the company claims initial successes, recent reports suggest Broadcom is dissatisfied with Intel’s 18A wafer test results, which have not yet met mass production standards.
Additionally, in a recent meeting, Intel discussed the rules around receiving chip subsidies. These funds will be distributed in stages based on the company’s progress, including plant construction, equipment installation, wafer output, and securing customers. The cancellation of the 20A process could affect the amount of government subsidies Intel receives, creating a significant funding challenge. This event is expected to impact Intel’s projected 2025 gross margins and operating expenses. Furthermore, it is believed that the AI CPU Arrow Lake could see decreased sales in mid- and low-end segments due to reduced competitiveness resulting from outsourcing production.
Intel missed the opportunity to secure a major contract with Sony for PlayStation due to high production costs.
In 2022, Intel lost the chance to design and manufacture chips for the Sony PlayStation 6, a significant setback in its efforts to grow its foundry business. Intel was competing with AMD and TSMC for this contract, which was valued in the billions of dollars. Despite prolonged discussions with Sony, Intel was unable to reach an agreement due to pricing differences, allowing AMD to successfully secure the contract.
This contract could have provided Intel with stable long-term revenue and bolstered its emerging semiconductor foundry business. However, concerns over backward compatibility, stemming from AMD’s involvement in previous PlayStation chip designs, were a key factor in Sony’s decision on its new foundry partner. The loss of this deal has exacerbated Intel’s difficulties in competing with Nvidia and AMD in the AI chip market and in attracting customers to adopt its advanced 18A process.
Intel is currently facing challenges, including large-scale layoffs and internal discussions about the future of certain business units, such as halting the construction of a factory in Germany and possibly spinning off its foundry business. Securing this contract with Sony could have helped Intel establish a stronger foothold in the chip manufacturing market, but the company is still searching for high-profile clients to drive the growth of its foundry operations.
Thanks for spending your valuable time with us! If you like our content, please like and subscribe to our Youtube channel to get more valuable content.
Furthermore, please visit our website sunfortzone.com for more data-driven insights, and join our Discord Server to discuss with other investors.
If you’ve learned something from our productions, please click the inclusive link down below to open an Interactive Brokers account for free. Your actions means a world to us!
When you open an account through the referral link above, you will receive 1 IBKR stock worth $1 USD for every $100 deposited, with a maximum value of $1,000 in IBKR stocks.
What’s your idea? please leave a comment below! We would like to learn something from you as well!